Appearance
数据结构&排序算法
数组
- 数组是一种线性的数据结构
- 优点:查找特定的元素特别快,通过索引下标查找元素,时间复杂度 O(1)
- 缺点:需要在内存中开辟连续的空间,当达到上限的时候,需要开辟 2 倍的空间,在把之前的数组拷贝过去,在头部增加、删除元素特别慢,因为每一个元素都需要位移
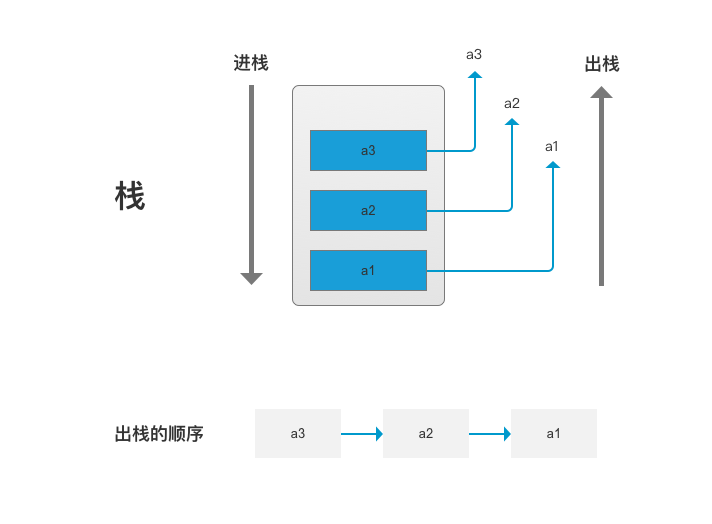
栈
- 栈是一种受限的数据结构,可以用数组或者链表来实现
- 特点:后进的先出,分为进栈和出栈,只能从栈顶一端进行操作,不能跨级
js
class Stack {
constructor() {
this.items = [];
}
// 进栈
push(element) {
this.items.push(element);
}
// 出栈
pop() {
return this.items.pop();
}
// 查看栈顶元素
peek() {
return this.items[this.items.length - 1];
}
// 获取栈中元素的个数
size() {
return this.items.length;
}
// 判断栈中的元素是否为空
isEmpty() {
return this.items.length === 0;
}
toString() {
return this.items.join(",");
}
}十进制转二进制
js
function dec2bin(decNumer) {
let stack = new Stack();
let n = decNumer;
while (n > 0) {
n = Math.floor(n / 2);
stack.push(n % 2);
}
let binayriStrng = "";
while (!stack.isEmpty()) {
binayriStrng = binayriStrng + "" + stack.pop();
}
return binayriStrng;
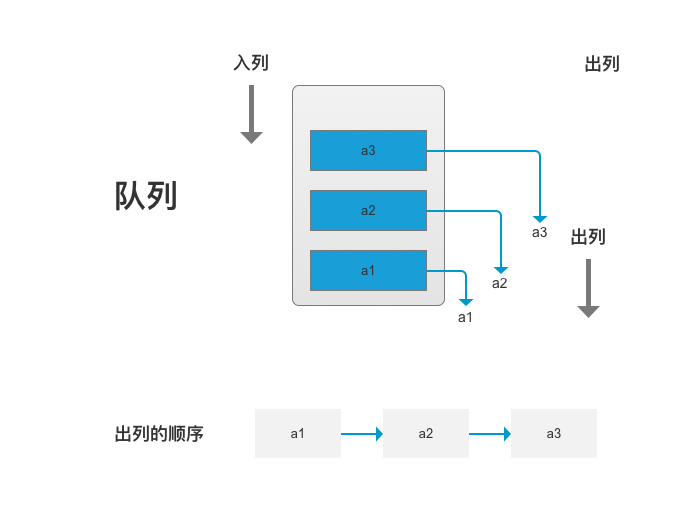
}队列
- 队列是一种受限的数据结构
- 特点:队列是从 2 端进行操作,一边进一边出,先进的先出,在加入队列的时候可以设置优先级,优先级越高位置越前
普通队列
js
class Queue {
constructor() {
this.items = [];
}
// 入列
enqueue(element) {
this.items.push(element);
}
// 出列
dequeue() {
return this.items.shift();
}
// 查看队列顶元素
front() {
return this.items[0];
}
// 获取队列中元素的个数
size() {
return this.items.length;
}
// 判断队列中的元素是否为空
isEmpty() {
return this.items.length === 0;
}
toString() {
return this.items.join(",");
}
}优先级队列
js
class PriorityQueue {
constructor() {
this.items = [];
}
// 入列
enqueue(element, priority) {
let enqueueItem = { element, priority };
if (this.isEmpty()) {
this.items.push(enqueueItem);
} else {
let hasAdd = false;
for (let index = 0; index < this.items.length; index++) {
// 数组越小优先级越高
if (priority < this.items[index].priority) {
this.items.splice(index, 0, enqueueItem);
hasAdd = true;
break;
}
}
// 遍历结束还未插入
if (!hasAdd) {
this.items.push(enqueueItem);
}
}
}
// 出列
dequeue() {
return this.items.shift();
}
// 查看队列顶元素
front() {
return this.items[0];
}
// 获取队列中元素的个数
size() {
return this.items.length;
}
// 判断队列中的元素是否为空
isEmpty() {
return this.items.length === 0;
}
toString() {
return JSON.stringify(this.items);
}
}js
// 有n个人,从1到y开始数数,每次数到y的人被淘汰,请问最后一个人谁,在原来的什么位置
function game(nameList, num) {
let queue = new Queue();
nameList.forEach((name) => {
queue.enqueue(name);
});
while (queue.size() > 1) {
for (var i = 1; i < num; i++) {
queue.enqueue(queue.dequeue());
}
console.log(queue.dequeue());
}
let index = nameList.indexOf(queue.toString());
console.log(`最终留下来的人${queue.toString()},原来${index}的位置`);
}
let nameList = ["lisi", "wangwu", "xianming", "tom"];
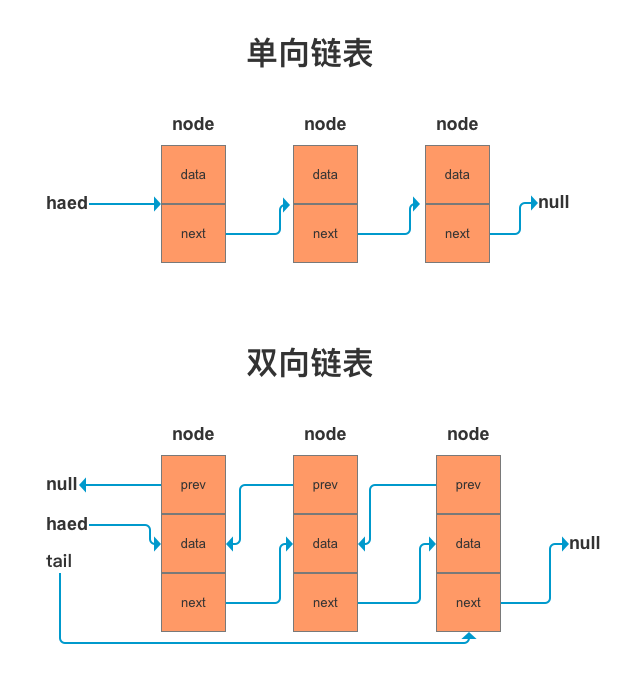
game(nameList, 3);链表
链表和数组一样,可以存储一系列的元素,但是底层实现和数组完全不同
特点:
- 1、内存空间不是连续的,可以动态的利用内存
- 2、在创建的时候不必确定大小,并且可以无限的延伸下去
- 3、插入和删除数据时间复杂度可以达到 O(1)
缺点:
- 无法直接通过索引直接找到对应的元素,需要遍历
单向链表
js
class LinkedList {
constructor() {
this.head = null;
this.length = 0;
}
// 链表元素
node(element) {
return {
element: element,
next: null,
};
}
// 链表尾部添加数组
append(element) {
let newNode = this.node(element);
// 如果没有数据
if (this.head == null) {
this.head = newNode;
} else {
// 遍历找到最后一个元素
let currentNode = this.head;
while (currentNode.next) {
currentNode = currentNode.next;
}
// 追加元素
currentNode.next = newNode;
}
this.length++;
}
// 指定的位置插入数据
insert(position, element) {
// 越界判断
if (position < 0 || position > this.length)
throw Error("LinkedListInsertBoundsException");
let newNode = this.node(element);
let currentNode = this.head;
let prevNode = null;
let index = 0;
// 如果是第一个
if (position === 0) {
newNode.next = currentNode;
this.head = newNode;
} else {
// 循环找到当前的要插入的位置
while (index < position) {
prevNode = currentNode;
currentNode = currentNode.next;
index++;
}
// 改变指针指向
newNode.next = currentNode;
prevNode.next = newNode;
}
this.length++;
return true;
}
// 根据指定的位置删除元素
removeAt(position) {
// 越界判断
if (position < 0 || position >= this.length)
throw Error("LinkedListInsertBoundsException");
let currentNode = this.head;
let prevNode = null;
let index = 0;
// 如果是第一个
if (position === 0) {
this.head = currentNode.next;
} else {
// 循环找到当前的要删除的位置
while (index < position) {
prevNode = currentNode;
currentNode = currentNode.next;
index++;
}
// 改变指针指向
prevNode.next = currentNode.next;
}
this.length--;
return currentNode.element;
}
// 根据元素去查找元素指定的位置
indexOf(element) {
let currentNode = this.head;
let index = 0;
while (currentNode) {
if (currentNode.element === element) {
return index;
}
currentNode = currentNode.next;
index++;
}
return -1;
}
// 根据元素删除元素
remove(element) {
let position = this.indexOf(element);
return this.removeAt(position);
}
toString() {
let currentNode = this.head;
let nodeStr = "";
while (currentNode) {
nodeStr += "|" + currentNode.element;
currentNode = currentNode.next;
}
return nodeStr.slice(1);
}
isEmpty() {
return this.length === 0;
}
size() {
return this.length;
}
// 查询头部元素
getFirst() {
return this.head.element;
}
}反转链表
js
function reverseLinkedListIterative(head) {
let preNode = null; // 上一个
let currentNode = head; // 当前的
while (currentNode) {
let nextNode = currentNode.next; // 保留后续的链表,防止冲断
currentNode.next = preNode; // 让下一个节点,指向上一个节点
preNode = currentNode; // 让上一个节点指向当前的节点
currentNode = nextNode; // 继续循环
}
return preNode;
}
console.log(reverseLinkedListIterative(linkedList.head));双向链表
js
class DoubleLinkedList {
constructor() {
this.head = null;
this.tail = null;
this.length = 0;
}
// 链表元素
node(element) {
return {
element: element,
prev: null,
next: null,
};
}
// 二分查找
binarySearch(position) {
if (this.length / 2 > position) {
return {
type: "front",
position: position,
};
} else {
return {
type: "back",
position: this.length - position,
};
}
}
// 链表尾部添加数组
append(element) {
let newNode = this.node(element);
// 如果没有数据
if (this.head == null) {
this.head = newNode;
this.tail = newNode;
} else {
// 遍历找到最后一个元素
let currentNode = this.head;
while (currentNode.next) {
currentNode = currentNode.next;
}
// 追加元素
newNode.prev = currentNode;
currentNode.next = newNode;
this.tail = newNode;
}
this.length++;
}
// 指定的位置插入数据
insert(position, element) {
// 越界判断
if (position < 0 || position > this.length)
throw Error("LinkedListInsertBoundsException");
let newNode = this.node(element);
// 如果是第一个
if (position === 0) {
// 数据为空
if (this.head == null) {
this.head = newNode;
this.tail = newNode;
} else {
this.head.prev = newNode;
newNode.next = this.head;
this.head = newNode;
}
} else if (position === this.length) {
// 如果是最后一个
this.tail.next = newNode;
newNode.prev = this.tail;
this.tail = newNode;
} else {
let previous = null;
let currentNode = null;
let binarySearch = this.binarySearch(position);
let index = 0;
// 正向
if (binarySearch.type === "front") {
currentNode = this.head;
// 循环找到当前的要插入的位置
while (index < position) {
previous = currentNode;
currentNode = currentNode.next;
index++;
}
// 交换节点的指向顺序
newNode.next = currentNode;
newNode.prev = previous;
currentNode.prev = newNode;
previous.next = newNode;
} else {
// 反向
currentNode = this.tail;
while (index < binarySearch.position) {
previous = currentNode;
currentNode = currentNode.prev;
index++;
}
// 交换节点的指向顺序
newNode.next = previous;
newNode.prev = currentNode;
currentNode.next = newNode;
previous.prev = newNode;
}
}
this.length++;
return true;
}
// 根据指定的位置删除元素
removeAt(position) {
// 越界判断
if (position < 0 || position >= this.length)
throw Error("LinkedListInsertBoundsException");
let currentNode = this.head;
// 如果是第一个
if (position === 0) {
// 只有一个数组
if (this.length === 1) {
this.head = null;
this.tail = null;
} else {
this.head = this.head.next;
this.head.prev = null;
}
} else if (position === this.length - 1) {
// 如果最后一个
currentNode = this.tail;
this.tail = this.tail.prev;
this.tail.next = null;
} else {
let previous = null;
let binarySearch = this.binarySearch(position);
let index = 0;
if (binarySearch.type === "front") {
// 正向
while (index < position) {
previous = currentNode;
currentNode = currentNode.next;
index++;
}
previous.next = currentNode.next;
currentNode.next.prev = previous;
this.length--;
return currentNode.element;
} else {
currentNode = this.tail;
// 反向
while (index < binarySearch.position) {
previous = currentNode;
currentNode = currentNode.prev;
index++;
}
currentNode.next = previous.next;
previous.next.prev = currentNode;
this.length--;
return previous.element;
}
}
}
// 根据元素去查找元素指定的位置
indexOf(element) {
let currentNode = this.head;
let index = 0;
while (currentNode) {
if (currentNode.element === element) {
return index;
}
currentNode = currentNode.next;
index++;
}
return -1;
}
// 根据元素删除元素
remove(element) {
let position = this.indexOf(element);
return this.removeAt(position);
}
isEmpty() {
return this.length === 0;
}
size() {
return this.length;
}
// 查询头部元素
getHead() {
return this.head.element;
}
// 查询尾部元素
getTail() {
return this.tail.element;
}
// 正向遍历
forwardString() {
let currentNode = this.head;
let nodeStr = "";
while (currentNode) {
nodeStr += "|" + currentNode.element;
currentNode = currentNode.next;
}
return nodeStr.slice(1);
}
// 反向遍历
reverseString() {
let currentNode = this.tail;
let nodeStr = "";
while (currentNode) {
nodeStr += "|" + currentNode.element;
currentNode = currentNode.prev;
}
return nodeStr.slice(1);
}
toString() {
return this.forwardString();
}
}集合
- 集合和数组内似,可以存储多个数据,它的无序的,并且不能重复(后添加的会覆盖前面的)
js
class Set {
constructor() {
this.items = {};
}
// 判断集合中是否有某个元素
has(value) {
return this.items.hasOwnProperty(value);
}
// 向集合中添加元素
add(value) {
this.items[value] = value;
return true;
}
// 从集合中删除某个元素
remove(value) {
if (this.has(value)) {
delete this.items[value];
return true;
}
return false;
}
// 清空集合中所有的元素
clear() {
this.items = {};
}
// 获取集合的大小
size() {
return Object.keys(this.items).length;
}
// 获取集合中所有的值
values() {
return Object.keys(this.items);
}
}字典
- 字典,可以存储多个数据,它的无序的,并且不能重复((后添加的会覆盖前面的)key,value 形式)
js
class Dictionay {
constructor() {
this.items = {};
}
// 判断字典中是否包含某个key
has(key) {
return this.items.hasOwnProperty(key);
}
// 在字典中添加键值对
set(key, value) {
this.items[key] = value;
return true;
}
// 根据key去获取value
get(key) {
return this.has(key) ? this.items[key] : undefined;
}
// 从字典中移除元素
remove(key) {
if (this.has(key)) {
delete this.has(key);
return true;
}
return false;
}
// 获取所有的keys
keys() {
return Object.keys(this.items);
}
// 获取所有的value
values() {
return Object.values(this.items);
}
// size方法
size() {
return this.keys().length;
}
// clear方法
clear() {
this.items = {};
}
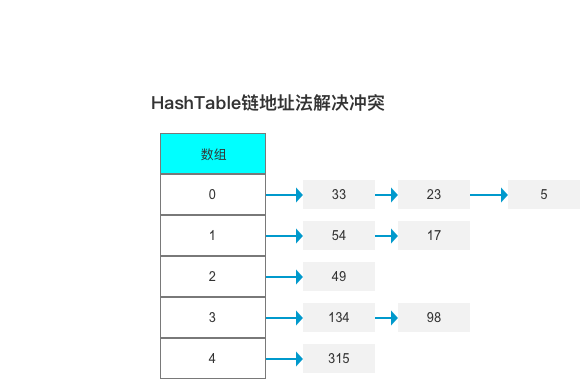
}哈希表
- 特点:增加和删除都比较高,可以达到瞬间查找
- 缺点:无法直接进行遍历,元素不能重复
- 实现原理:利用数组实现,当在存值的时候,首先把 key 作为条件,生成一个 hashCode 码,hashCode 码作为数组的索引,插入到二维数组中(链地址法解决冲突)
js
class HashTable {
constructor() {
this.storage = [];
this.count = 0;
this.limit = 8;
}
// 哈希函数
hashFunc(str, max) {
let hashCode = 0;
// 霍纳算法, 来计算hashCode的数值
for (let index = 0; index < str.length; index++) {
// 质树有利于平均分布
hashCode = 37 * hashCode + str.charCodeAt(index);
}
//压缩到指定的索引范围
return hashCode % max;
}
// 判断是否是质数
isPrime(num) {
let temp = parseInt(Math.sqrt(num));
for (let index = 2; index <= temp; index++) {
if (num % index === 0) {
return false;
}
return true;
}
}
getPrime(num) {
if (!this.isPrime(num)) return this.getPrime(++num);
return num;
}
put(key, value) {
// 生成索引
let index = this.hashFunc(key, this.limit);
let bucket = this.storage[index];
if (bucket === undefined) {
bucket = [];
this.storage[index] = bucket;
}
let override = false;
for (let i = 0; i < bucket.length; i++) {
let temp = bucket[i];
// 判断是否存在
if (temp[0] === key) {
temp[1] = value;
override = true;
}
}
// 不存在直接追加
if (!override) {
bucket.push([key, value]);
this.count++;
// 总长度超过限制的75%,需要扩容
if (this.count > this.limit * 0.75) {
this.resize(this.getPrime(this.limit * 2));
}
}
}
get(key) {
let index = this.hashFunc(key, this.limit);
let bucket = this.storage[index];
if (bucket === undefined) {
return null;
}
for (let i = 0; i < bucket.length; i++) {
const temp = bucket[i];
if (temp[0] === key) {
return temp[1];
}
}
return null;
}
remove(key) {
let index = this.hashFunc(key, this.limit);
let bucket = this.storage[index];
if (bucket == undefined) {
return null;
}
for (let i = 0; i < bucket.length; i++) {
const temp = bucket[i];
if (temp[0] === key) {
bucket.splice(i, 1);
this.count--;
// 总长度小于限制的25%,需要缩小数组的容量
if (this.limit > 7 && this.count < this.limit * 0.25) {
this.resize(this.getPrime(Math.floor(this.limit / 2)));
}
return temp[1];
}
return null;
}
}
resize(newLimit) {
let oldStorage = this.storage;
// 属性重置
this.storage = [];
this.limit = newLimit;
this.count = 0;
for (let index = 0; index < oldStorage.length; index++) {
let arr = oldStorage[index];
if (arr !== undefined) {
arr.forEach((bucket) => {
this.put(bucket[0], bucket[1]);
});
}
}
}
isEmpty() {
return this.count == 0;
}
size() {
return this.count;
}
}二叉树
树的定义
- 树(Tree): n(n≥0)个结点构成的有限集合。
- 当 n=0 时,称为空树;
- 对于任一棵非空树(n> 0),它具备以下性质:
- 树中有一个称为“根(Root)”的特殊结点,用 r 表示;
- 其余结点可分为 m(m>0)个互不相交的有限集 T1,T2,... ,Tm,其中每个集合本身又是一棵树,称为原来树的“子树(SubTree)”
- 注意:
- 子树之间不可以相交
- 除了根结点外,每个结点有且仅有一个父结点;
树的术语
- 1.结点的度(Degree):结点的子树个数.
- 2.树的度:树的所有结点中最大的度数. (树的度通常为结点的个数 N-1)
- 3.叶结点(Leaf):度为 0 的结点. (也称为叶子结点)
- 4.父结点(Parent):有子树的结点是其子树的根结点的父结点
- 5.子结点(Child):若 A 结点是 B 结点的父结点,则称 B 结点是 A 结点的子结点;子结点也称孩子结点。
- 6.兄弟结点(Sibling):具有同一父结点的各结点彼此是兄弟结点。
- 7.路径和路径长度:从结点 n1 到 nk 的路径为一个结点序列 n1 , n2,… , nk, ni 是 ni+1 的父结点。路径所包含边的个数为路径的长度。
- 8.结点的层次(Level):规定根结点在 1 层,其它任一结点的层数是其父结点的层数加 1。
- 9.树的深度(Depth):树中所有结点中的最大层次是这棵树的深度。
二叉树的特性
一个二叉树第 i 层的最大结点数为:2^(i-1), i >= 1;
深度为 k 的二叉树有最大结点总数为: 2^k - 1, k >= 1;
对任何非空二叉树 T,若 n0 表示叶结点的个数、n2 是度为 2 的非叶结点个数,那么两者满足关系 n0 = n2 + 1。
完美二叉树(Perfect Binary Tree) , 也称为满二叉树(Full Binary Tree)
在二叉树中, 除了最下一层的叶结点外, 每层节点都有 2 个子结点, 就构成了满二叉树.
完全二叉树(Complete Binary Tree)
除二叉树最后一层外, 其他各层的节点数都达到最大个数.
且最后一层从左向右的叶结点连续存在, 只缺右侧若干节点.
完美二叉树是特殊的完全二叉树.
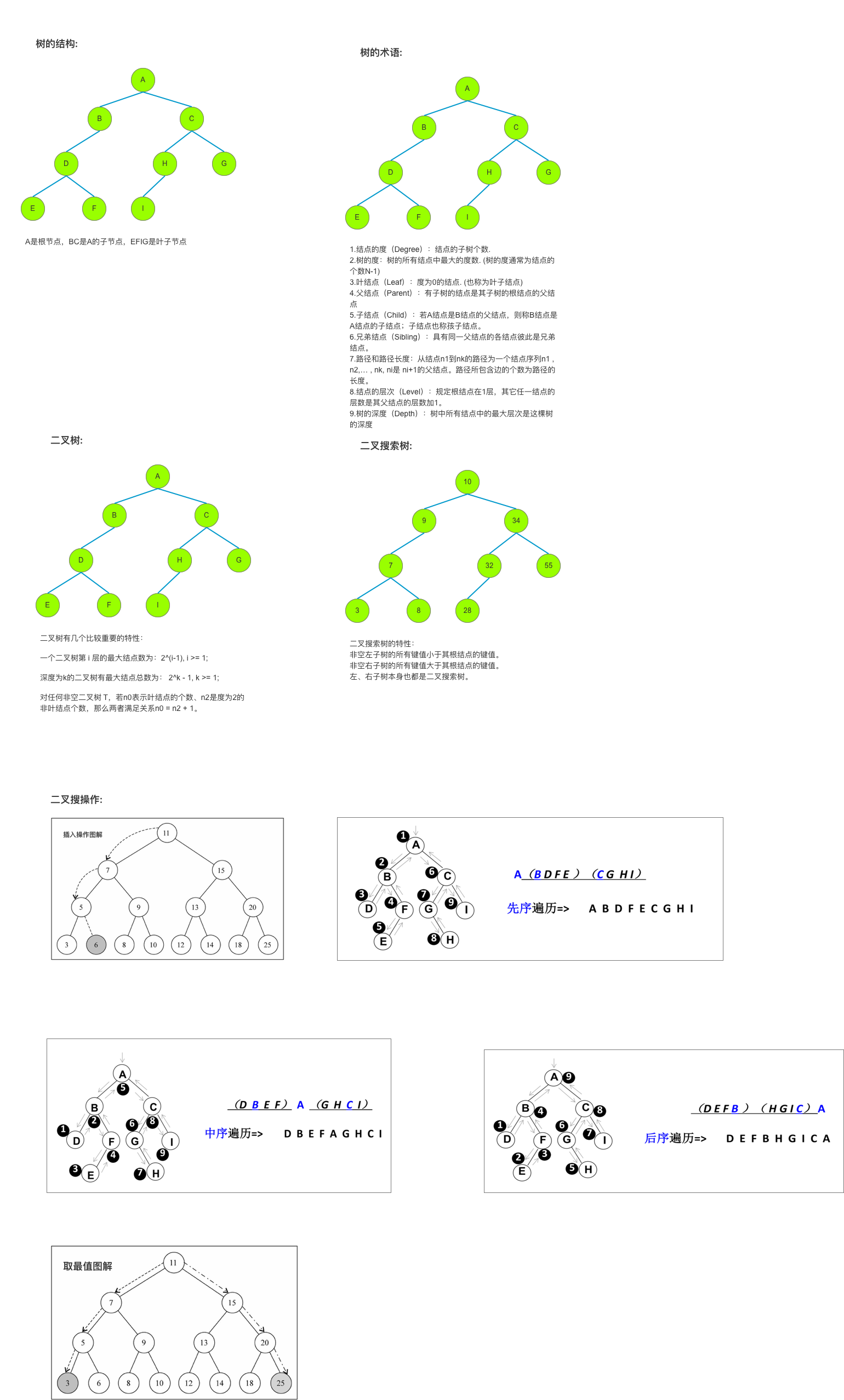
二叉搜索树的特点:
二叉搜索树的特点就是相对较小的值总是保存在左结点上, 相对较大的值总是保存在右结点上.
js
class BinarySerachTree {
constructor() {
this.root = null;
}
node(key) {
return {
key: key,
left: null,
right: null,
};
}
// 插入操作
insert(key) {
let newNode = this.node(key);
if (this.root === null) {
this.root = newNode;
} else {
this.insertNode(this.root, newNode);
}
}
insertNode(node, newNode) {
// 小于向左找
if (newNode.key < node.key) {
// 如果没左节点
if (node.left === null) {
node.left = newNode;
} else {
// 如果有左节点,递归
this.insertNode(node.left, newNode);
}
} else {
if (node.right === null) {
node.right = newNode;
} else {
this.insertNode(node.right, newNode);
}
}
}
/**
* 深度优先遍历-先序遍历
* ①访问根结点;
* ②先序遍历其左子树;
* ③先序遍历其右子树
*/
preOrderTraverse(handler) {
this.preOrderTraverseNode(this.root, handler);
}
preOrderTraverseNode(node, handler) {
if (node !== null) {
handler(node.key);
this.preOrderTraverseNode(node.left, handler);
this.preOrderTraverseNode(node.right, handler);
}
}
/**
* 深度优先遍历-中序遍历
* ①中序遍历其左子树;
* ②访问根结点;
* ③中序遍历其右子树。
*/
inOrderTraversal(handler) {
this.inOrderTraversalNode(this.root, handler);
}
inOrderTraversalNode(node, handler) {
if (node !== null) {
this.inOrderTraversalNode(node.left, handler);
handler(node.key);
this.inOrderTraversalNode(node.right, handler);
}
}
/**
* 深度优先遍历-后序遍历
* ①后序遍历其左子树;
* ②后序遍历其右子树;
* ③访问根结点。
*/
postOrderTraversal(handler) {
this.postOrderTraversalNode(this.root, handler);
}
postOrderTraversalNode(node, handler) {
if (node !== null) {
this.postOrderTraversalNode(node.left, handler);
this.postOrderTraversalNode(node.right, handler);
handler(node.key);
}
}
// 删除节点
remove(key) {
let current = this.root;
let parent = null;
let isLeftChild = true;
while (current.key != key) {
parent = current;
if (key > current.key) {
isLeftChild = false;
current = current.right;
} else {
isLeftChild = true;
current = current.left;
}
// 如果current已经指向null, 那么说明没有找到要删除的数据
if (current === null) return false;
}
// 情况一:如果是叶节点
if (current.left === null && current.right === null) {
// 正好的根节点
if (current === this.root) {
this.root = null;
} else if (isLeftChild) {
parent.left = null;
} else {
parent.right = null;
}
}
// 情况二:只有一个节点
else if (current.left === null) {
// 如果是根节点
if (current === this.root) {
this.root = current.right;
} else if (isLeftChild) {
parent.left = current.right;
} else {
parent.right = current.right;
}
} else if (current.right === null) {
// 如果是根节点
if (current === this.root) {
this.root = current.left;
} else if (isLeftChild) {
parent.left = current.left;
} else {
parent.right = current.left;
}
} else {
/**
* 删除有两个节点的节点(操作完成后还需要满足二叉搜索数的特性)
* 方案一:把当前要删除的左子数最大的提取上去(前驱)
* 方案二:把当前要删除的右子数最小的提取上去(后继)
*/
let successor = this.getSuccessor(current);
if (current === this.root) {
this.root = successor;
} else if (isLeftChild) {
parent.left = successor;
} else {
parent.right = successor;
}
successor.left = current.left;
}
return true;
}
// 找后继的方法
getSuccessor(delNode) {
let successorParent = delNode;
let successor = delNode;
let current = delNode.right; // 要从右子树开始找
while (current != null) {
successorParent = successor;
successor = current;
current = current.left;
}
// 如果提取上去的节点有子节点
if (successor != delNode.right) {
successorParent.left = successor.right;
successor.right = delNode.right;
}
return successor;
}
// 搜搜特定的值
search(key) {
let node = this.root;
while (node !== null) {
if (key < node.key) {
node = node.left;
} else if (key > node.key) {
node = node.right;
} else {
return node;
}
}
return null;
}
// 或取最小值
min() {
let node = this.root;
while (node.left !== null) {
node = node.left;
}
return node.key;
}
// 或取最大值
max() {
let node = this.root;
while (node.right !== null) {
node = node.right;
}
return node.key;
}
}
// 测试代码
var bst = new BinarySerachTree();
// 插入数据
bst.insert(10);
bst.insert(9);
bst.insert(34);
bst.insert(7);
bst.insert(3);
bst.insert(8);
bst.insert(32);
bst.insert(55);
bst.insert(28);
let stra = "";
console.log(bst.remove(10));
bst.preOrderTraverse((key) => {
stra = stra + " " + key;
});
console.log("先序", stra);
let strb = "";
bst.inOrderTraversal((key) => {
strb = strb + " " + key;
});
console.log("中序", strb);
let strc = "";
bst.postOrderTraversal((key) => {
strc = strc + " " + key;
});
console.log("后序", strc);冒泡排序
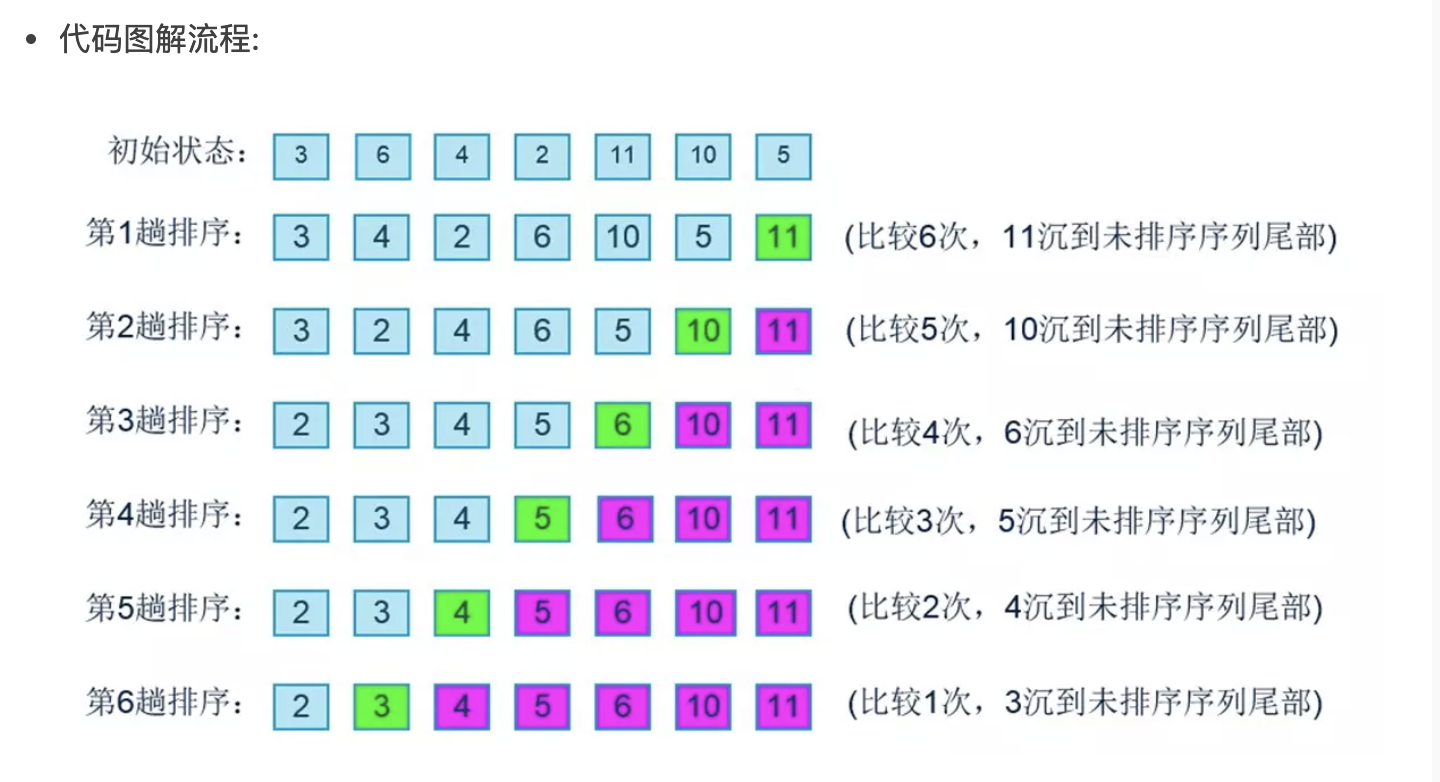
思路:
- 每相邻的二个元素进行比较如果大于就交换顺序
- 第一次找出最高的一位放置在末尾
- 第二次找出次高的一位放置在倒数第二,依次内推
代码实现:
- 外层循环控制每次对比的次数,对比的次数依次减少
- 内层循环两两进行对比,内外层循环结束顺序就依次排列好
时间复杂度:
- 对比的次数和交换的次数都是 O(N^2)
js
class ArrayList {
constructor() {
this.array = [];
}
insert(item) {
this.array.push(item);
}
toString() {
return this.array.join(",");
}
// 交换
swap(x, y) {
let temp = this.array[x];
this.array[x] = this.array[y];
this.array[y] = temp;
}
bubbleSort() {
let len = this.array.length;
for (let i = 0; i < len - 1; i++) {
for (let j = i + 1; j < len; j++) {
if (this.array[i] > this.array[j]) {
this.swap(i, j);
}
}
}
}
}
let arrayList = new ArrayList();
arrayList.insert(3);
arrayList.insert(6);
arrayList.insert(4);
arrayList.insert(2);
arrayList.insert(11);
arrayList.insert(10);
arrayList.insert(5);
arrayList.bubbleSort();
console.log(arrayList.toString()); // 2,3,4,5,6,10,11选择排序
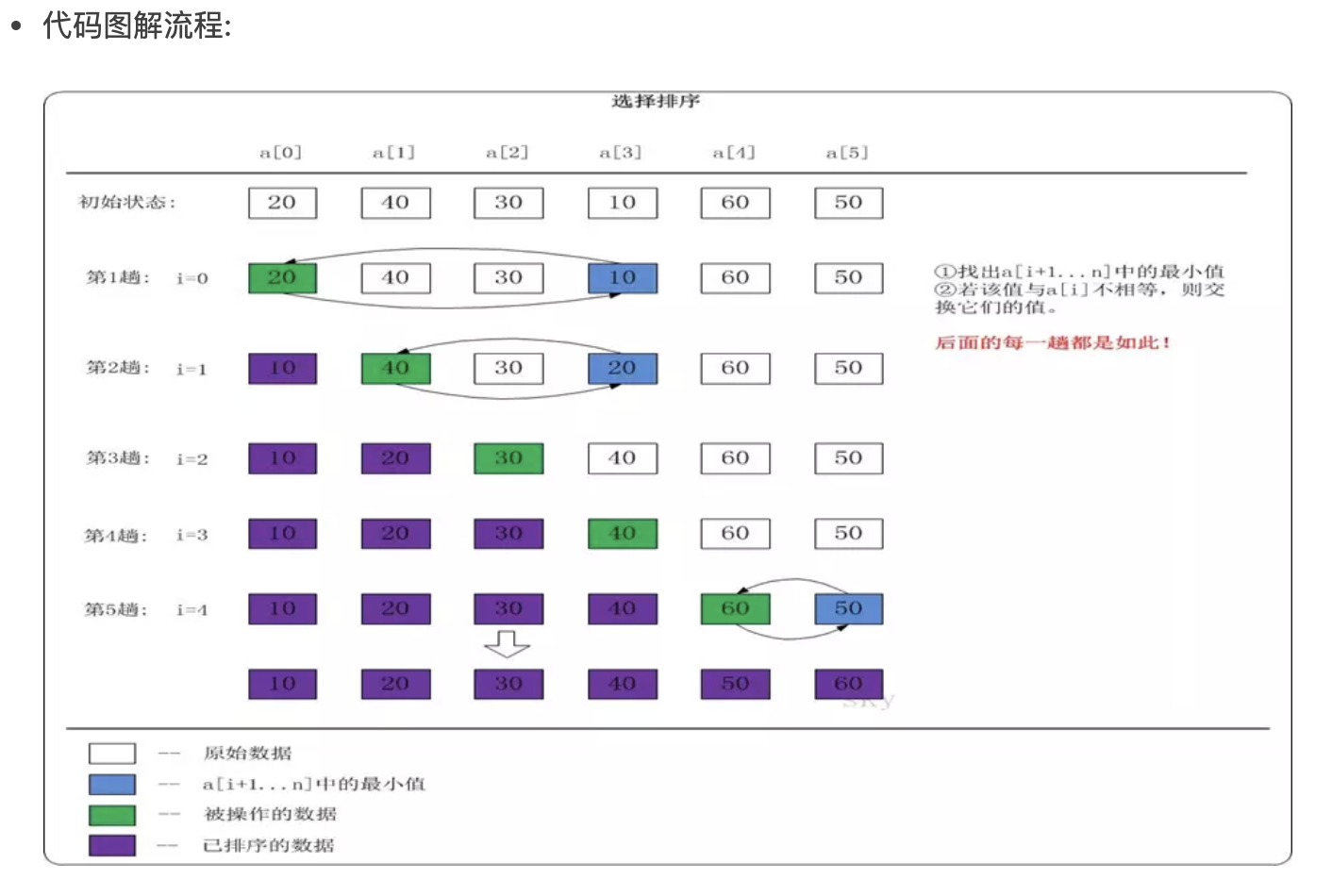
思路:
- 选择第一个索引的位置,依次和后面的进行比较
- 如果大于就交换它们的位置,循环到最后,就能确定最小的位置的索引
- 用最小位置的索引的值和第一个索引进行交换,依次内推
代码实现:
- 外层循环记录需要交换的索引位置,每次交换后需要从下一个索引开始,所以依次递增
- 内层循环依次进行对比找出最小的值的索引,内层循环结束后交换值位置
时间复杂度:
- 对比的次数 O(N^2)
- 交换的次数都是 O(N)
js
class ArrayList {
constructor() {
this.array = [];
}
insert(item) {
this.array.push(item);
}
toString() {
return this.array.join(",");
}
// 交换
swap(x, y) {
let temp = this.array[x];
this.array[x] = this.array[y];
this.array[y] = temp;
}
selectionSort() {
let len = this.array.length;
for (let i = 0; i < len - 1; i++) {
let min = i;
// 内循环找出最小的值的索引
for (let j = i + 1; j < len; j++) {
if (this.array[min] > this.array[j]) {
min = j;
}
}
// 交换
this.swap(i, min);
}
}
}
let arrayList = new ArrayList();
arrayList.insert(20);
arrayList.insert(40);
arrayList.insert(30);
arrayList.insert(10);
arrayList.insert(60);
arrayList.insert(50);
arrayList.selectionSort();
console.log(arrayList.toString()); // 10,20,30,40,50,60插入排序
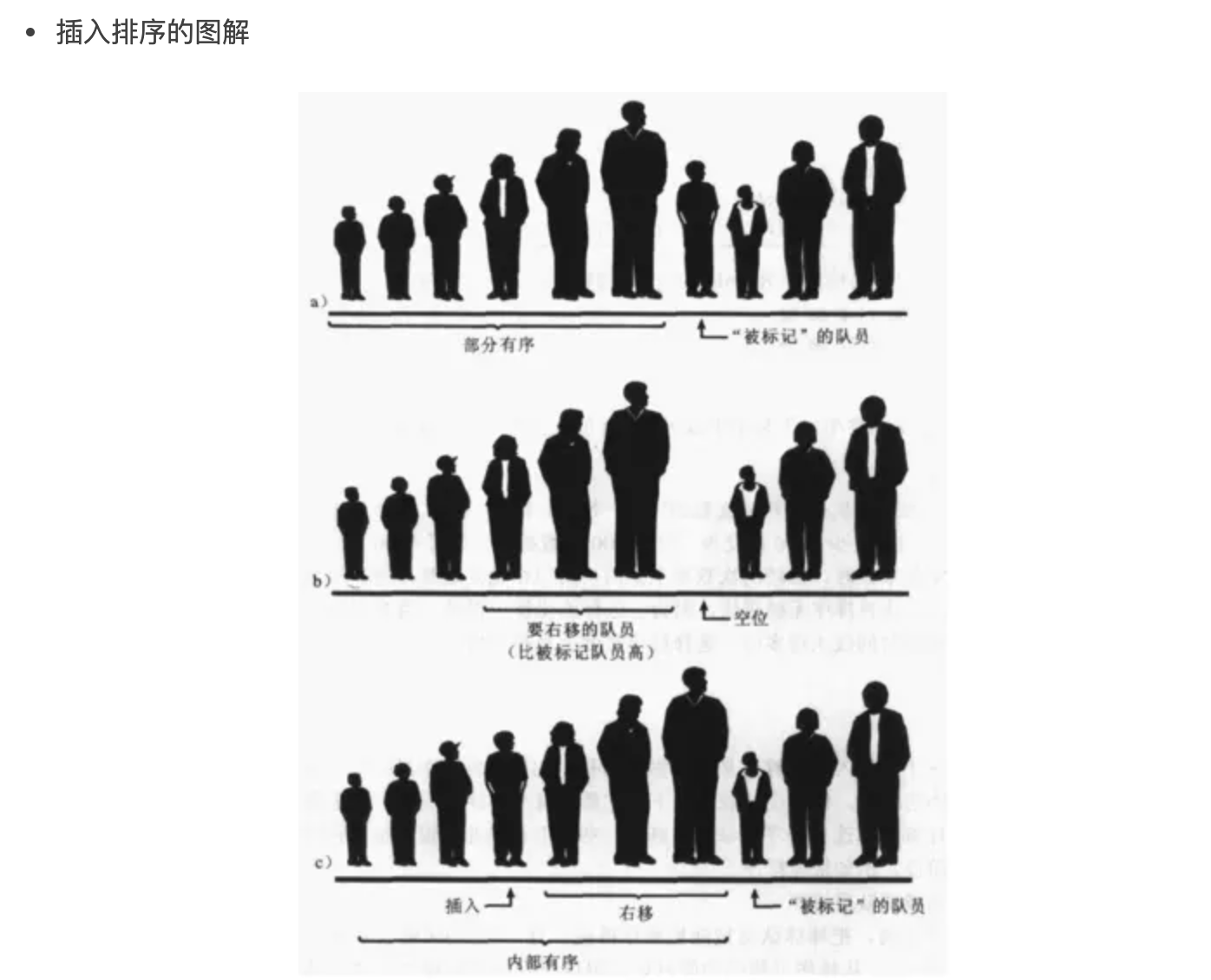
思路:
- 从下标一开始,默认 0 的位置可以看成局部有序
- 从第一个开始依次往前进行对比,大于就交换顺序,直到对比到第一个下标的位置
代码实现:
- 外层循环控制对比的次数,记录索引的位置和值,索引依次递增
- 内层循环进行对比,大于就直接赋值,并且记录索引的位置
- 内层循环结束后,录索引的位置进行赋值
时间复杂度:
- 对比的次数 O(N^2)
- 交换的次数都是 O(N)
js
class ArrayList {
constructor() {
this.array = [];
}
insert(item) {
this.array.push(item);
}
toString() {
return this.array.join(",");
}
// 交换
swap(x, y) {
let temp = this.array[x];
this.array[x] = this.array[y];
this.array[y] = temp;
}
insertionSort() {
const len = this.array.length;
for (let i = 1; i < len; i++) {
let j = i;
let temp = this.array[i];
while (j > 0 && this.array[j - 1] > temp) {
this.array[j] = this.array[j - 1];
j--;
}
this.array[j] = temp;
}
}
}
let array = new ArrayList();
array.insert(10);
array.insert(1);
array.insert(20);
array.insert(4);
array.insertionSort(array);
console.log(array.toString());希尔排序
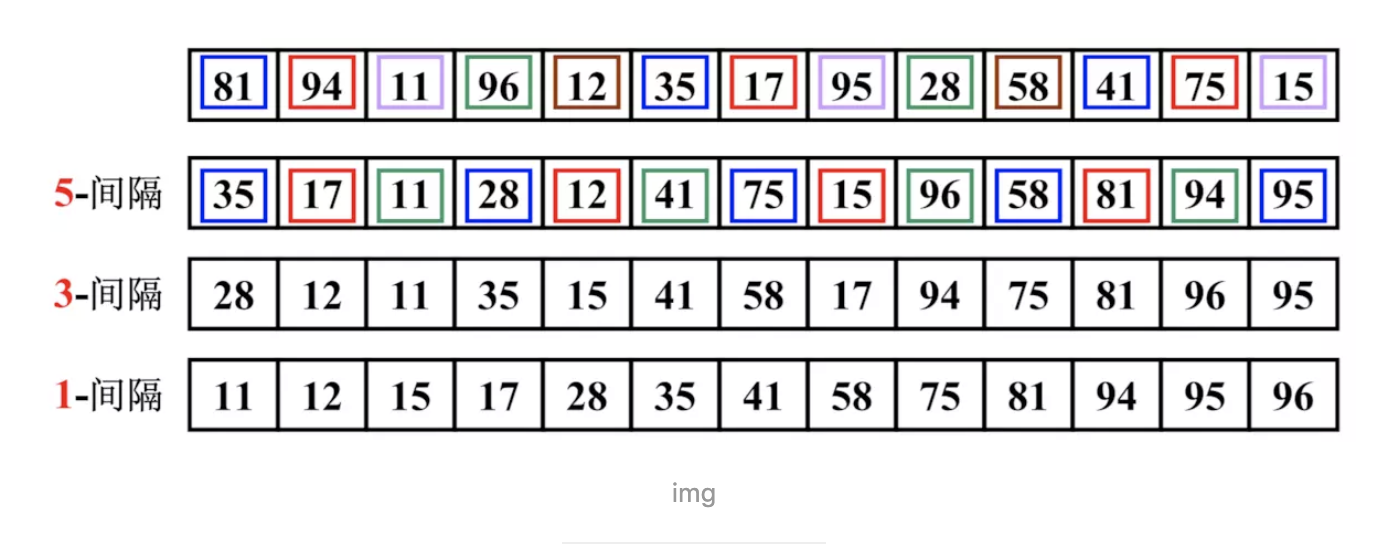
希尔排序(插入排序升级版)
- 首先获取一个增量
- 外层循环增量不断变小, 大于 0 就继续改变增量
- 内层循环实现了插入排序
时间复杂度:
- 最坏的情况 O(N^2)
js
class ArrayList {
constructor() {
this.array = [];
}
insert(item) {
this.array.push(item);
}
toString() {
return this.array.join(",");
}
// 交换
swap(x, y) {
let temp = this.array[x];
this.array[x] = this.array[y];
this.array[y] = temp;
}
shellSort() {
const len = this.array.length;
let gap = Math.floor(len / 2);
while (gap > 0) {
for (let i = gap; i < this.array.length; i++) {
let j = i;
let temp = this.array[i];
while (j > gap - 1 && this.array[j - gap] > temp) {
this.array[j] = this.array[j - gap];
j -= gap;
}
this.array[j] = temp;
}
gap = Math.floor(gap / 2);
}
}
}
let array = new ArrayList();
array.insert(10);
array.insert(1);
array.insert(20);
array.insert(4);
array.quickSort(array);
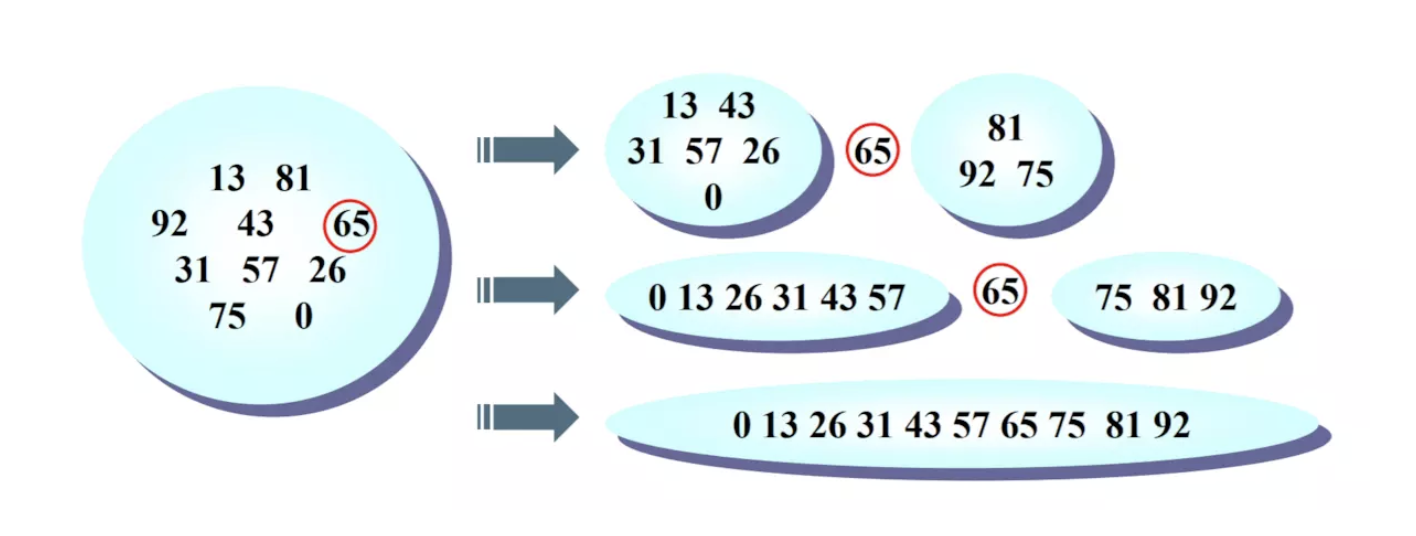
console.log(array.toString());快速排序
- 思路
- 选择第一位最为枢纽
- 从第二位开始进行遍历
- 比枢纽小的放在左边,小的放在右边,此时枢纽就是正确的位置
- 左边、右边也是一个数组,在进行递归,所有的递归结束后就排好顺序
- 时间复杂度
- O(N*logN)
js
class ArrayList {
constructor() {
this.array = [];
}
insert(item) {
this.array.push(item);
}
toString() {
return this.array.join(",");
}
quick(list) {
if (!Array.isArray(list)) {
return list;
}
if (list.length === 0) {
return [];
}
let pivot = list[0];
let mins = [];
let maxs = [];
for (let index = 1; index < list.length; index++) {
let item = list[index];
if (pivot > item) {
mins.push(item);
} else {
maxs.push(item);
}
}
return [...this.quick(mins), pivot, ...this.quick(maxs)];
}
quickSort() {
this.array = this.quick(this.array);
}
}
let array = new ArrayList();
array.insert(10);
array.insert(1);
array.insert(20);
array.insert(4);
array.quickSort();
console.log(array.toString());二分查找
思路
- 每次取从中间的位置开始
- 如果找到返回索引
- 如果中间的数值大,继续从左找
- 如果中间的数值小,继续从右找
- 循环结束后还未找到返回-1
时间复杂度
- O(N*logN)
js
class ArrayList {
constructor() {
this.array = [];
}
insert(item) {
this.array.push(item);
}
binarySearch(element) {
let minIndex = 0;
let maxIndex = this.array.length - 1;
let middleValue;
while (minIndex <= maxIndex) {
// 中间开始查找
let middleIndex = parseInt((minIndex + maxIndex) / 2);
middleValue = this.array[middleIndex];
if (middleValue === element) {
return middleIndex;
} else if (middleValue > element) {
// 左找
// 中间位置的前一个开始
maxIndex = middleIndex - 1;
} else {
// 中间位置的后一个开始
minIndex = middleIndex + 1; // 右找
}
}
return -1;
}
}
let array = new ArrayList();
array.insert(1);
array.insert(2);
array.insert(3);
array.insert(4);
array.insert(5);
array.insert(19);
console.log(array.binarySearch(119));深度优先(DFS)
- 深度优先搜索英文缩写为 DFS 即 Depth First Search
- 其过程简要来说是对每一个可能的分支路径深入到不能再深入为止,而且每个节点只能访问一次
- 应用场景
- React 虚拟 DOM 的构建
- React 的 fiber 树构建
实现思路
- 先访问根节点,如果有 children,遍历 children 节点,递归 dfs
js
// 对象的情况
function dfs(node) {
console.log(node.name);
node.children &&
node.children.forEach((child) => {
dfs(child);
});
}
let root = {
name: "A",
children: [
{
name: "B",
children: [{ name: "B1" }, { name: "B2" }],
},
{
name: "C",
children: [{ name: "C1" }, { name: "C2" }],
},
],
};
dfs(root); // A B B1 B2 C C1 C2js
// 数组的情况
function dfs(root) {
root &&
root.forEach((node) => {
console.log(node.name);
dfs(node.children);
});
}
let root = [
{
name: "A",
children: [
{
name: "B",
children: [{ name: "B1" }, { name: "B2" }],
},
{
name: "C",
children: [{ name: "C1" }, { name: "C2" }],
},
],
},
{
name: "A1",
children: [
{
name: "B1",
children: [{ name: "B11" }, { name: "B21" }],
},
{
name: "C1",
children: [{ name: "C11" }, { name: "C21" }],
},
],
},
];
dfs(root);广度优先(BFS)
- 宽度优先搜索算法(又称广度优先搜索),其英文全称是 Breadth First Search
- 算法首先搜索距离为 k 的所有顶点,然后再去搜索距离为 k+l 的其他顶点
实现思路(利用栈的特性)
- 1、首先创建一个数组,将根节点添加到数组中
- 2、进入 while 循环,每次取栈顶的节点,如果节点中有 children,遍历 children 节点,添加到数组中
js
// 对象的情况
function bfs(node) {
const stack = [];
stack.push(node);
let current = stack.shift();
while (current) {
console.log(current.name);
current.children &&
current.children.forEach((child) => {
stack.push(child);
});
current = stack.shift();
}
}
let root = {
name: "A",
children: [
{
name: "B",
children: [{ name: "B1" }, { name: "B2" }],
},
{
name: "C",
children: [{ name: "C1" }, { name: "C2" }],
},
],
};
bfs(root); // A B C B1 B2 C1 C2js
// 数组的情况
function bfs(root) {
root &&
root.forEach((node) => {
const stack = [];
stack.push(node);
let current = stack.shift();
while (current) {
console.log(current.name);
current.children &&
current.children.forEach((child) => {
stack.push(child);
});
current = stack.shift();
}
});
}
let root = [
{
name: "A",
children: [
{
name: "B",
children: [{ name: "B1" }, { name: "B2" }],
},
{
name: "C",
children: [{ name: "C1" }, { name: "C2" }],
},
],
},
{
name: "A1",
children: [
{
name: "B1",
children: [{ name: "B11" }, { name: "B21" }],
},
{
name: "C1",
children: [{ name: "C11" }, { name: "C21" }],
},
],
},
];
bfs(root);